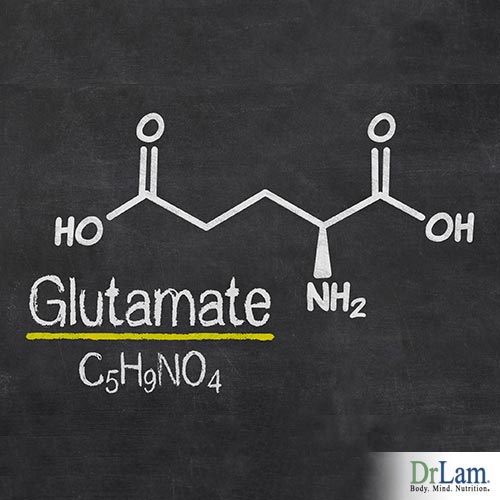
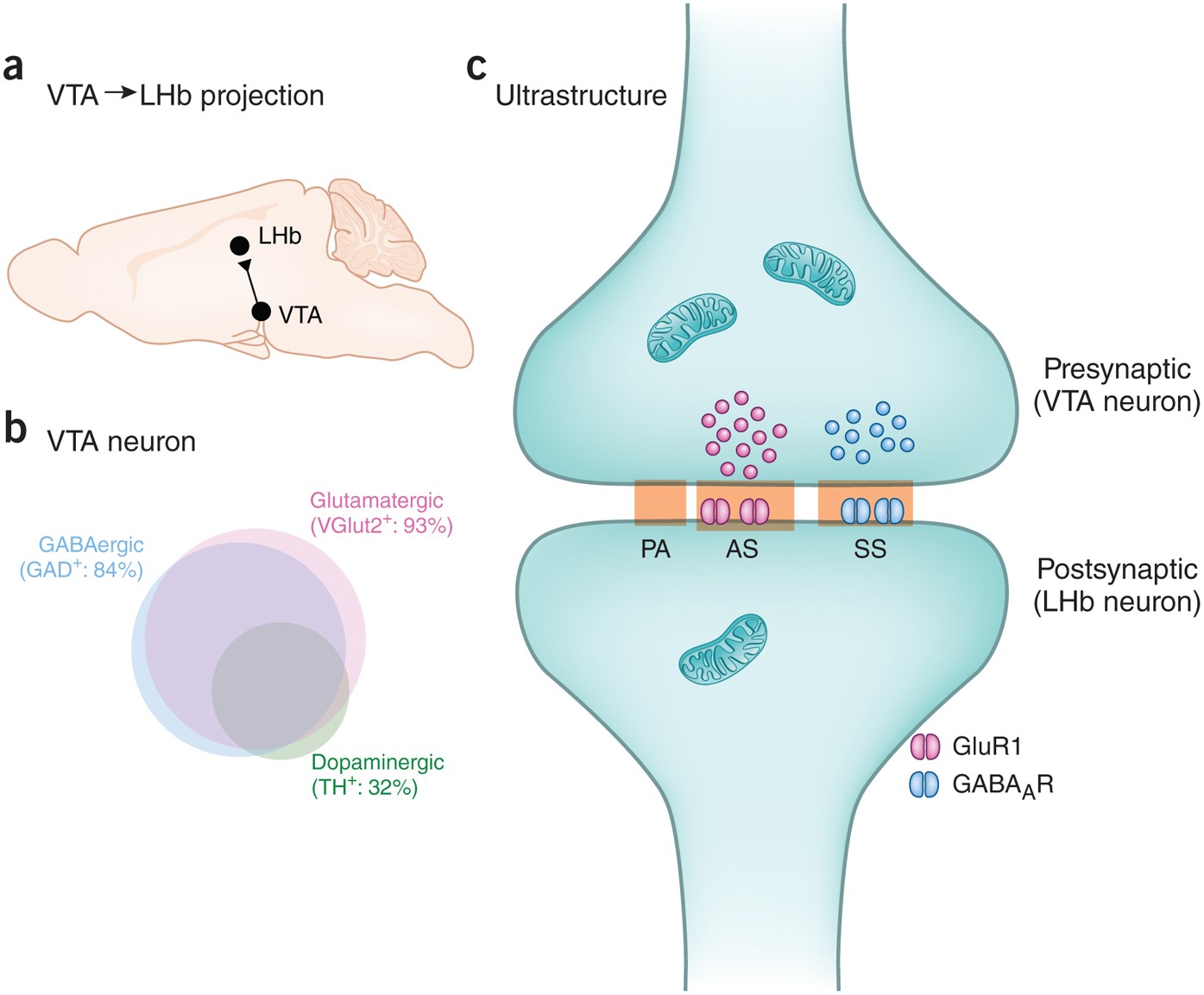
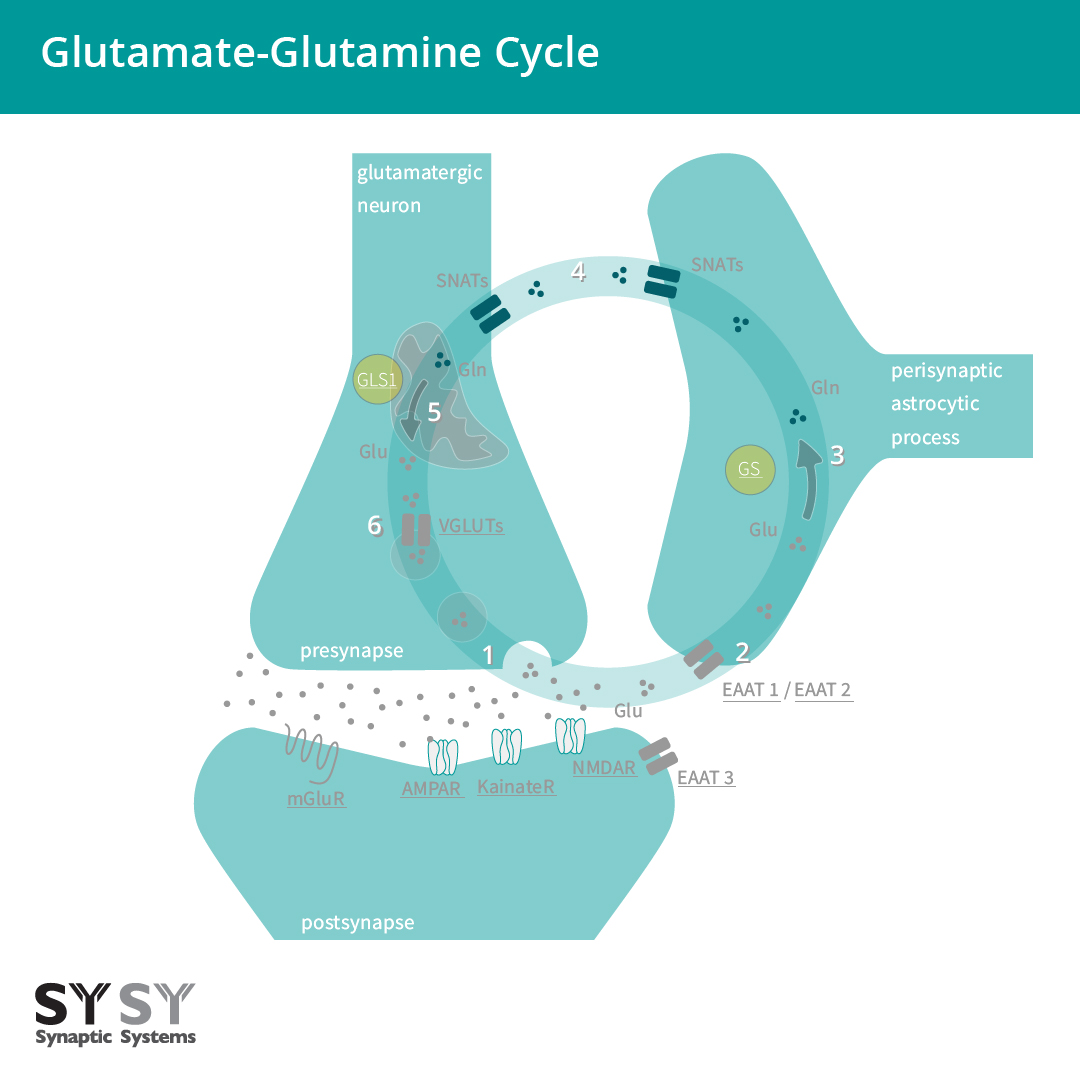
In the mammalian central nervous system (CNS), glutamate is the predominant excitatory neurotransmitter. It is estimated that more than half of all synapses release glutamate and that almost all excitatory neurons in the CNS are glutamatergic.

Glutamatergic and hypothetical aminergic tripartite synapses. The

Mechanisms of Glutamate Transport
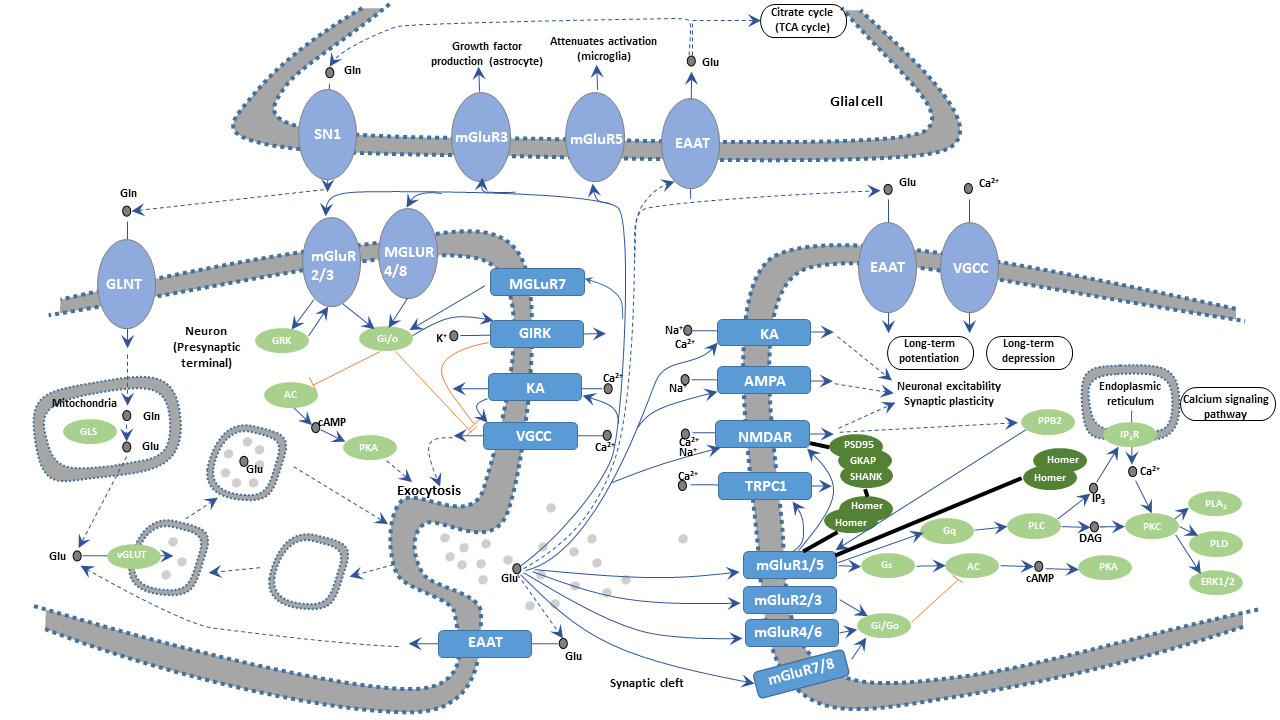
Glutamatergic synapse - CUSABIO
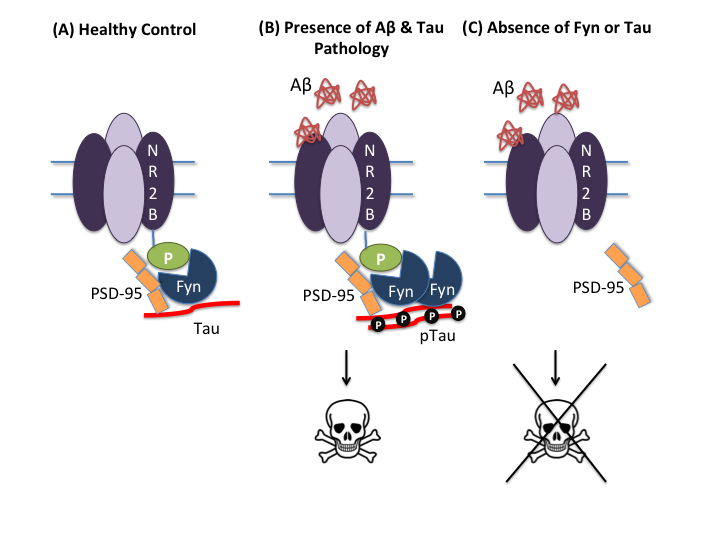
The Role of the Tripartite Glutamatergic Synapse in the Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease

JCI - Dysbindin-1 and schizophrenia: from genetics to neuropathology
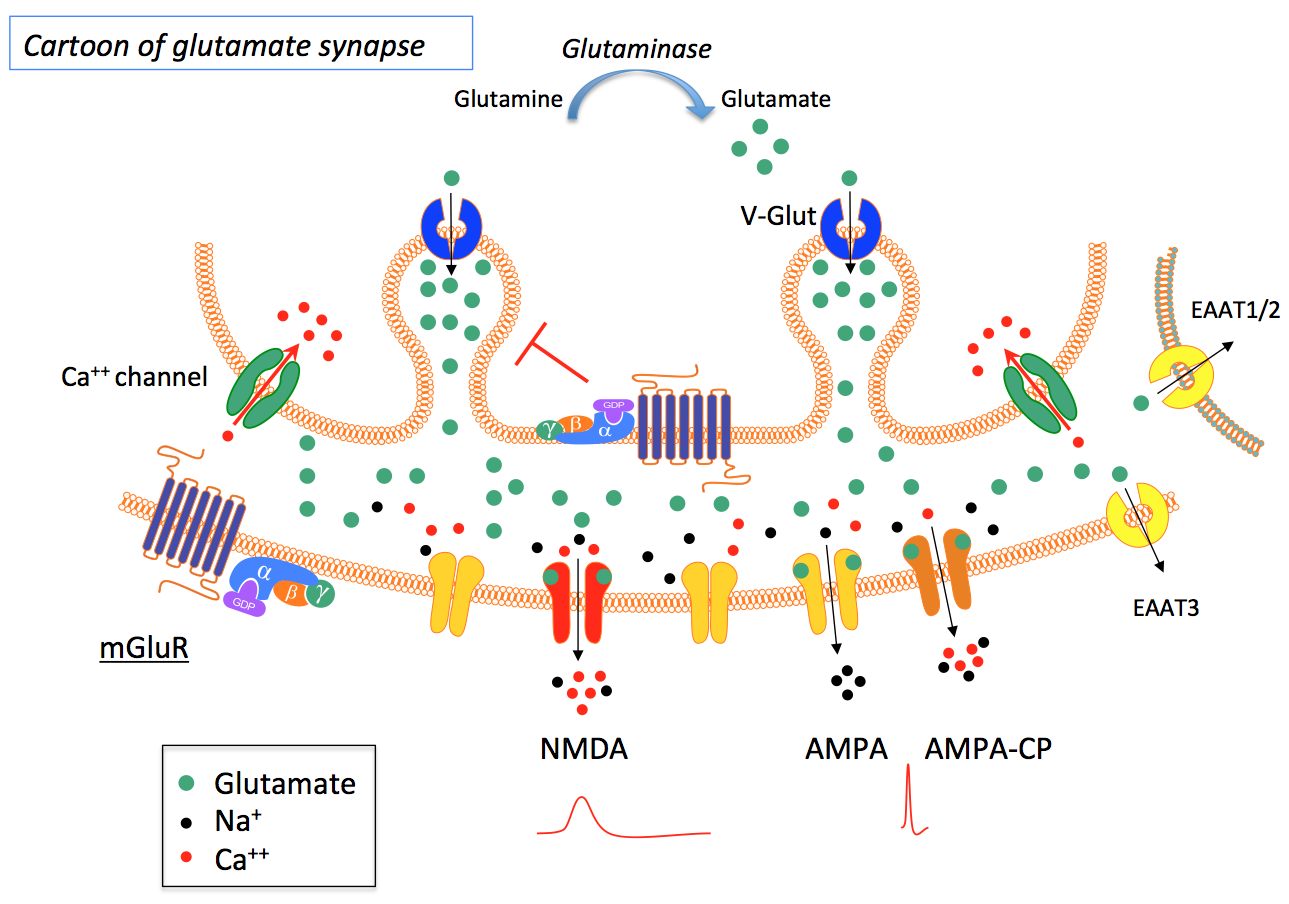
Ongoing Research Projects
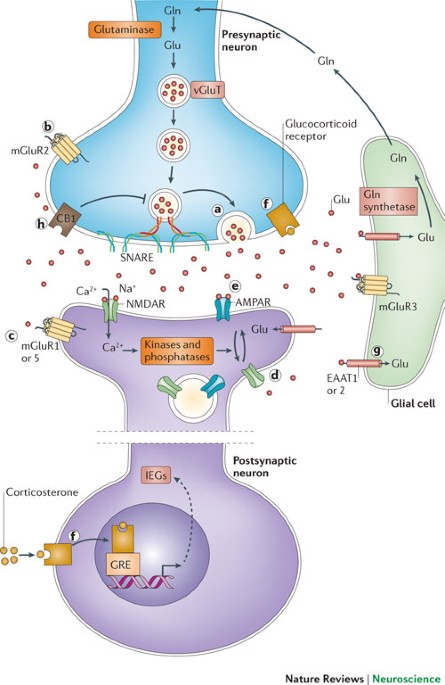
The stressed synapse: the impact of stress and glucocorticoids on glutamate transmission
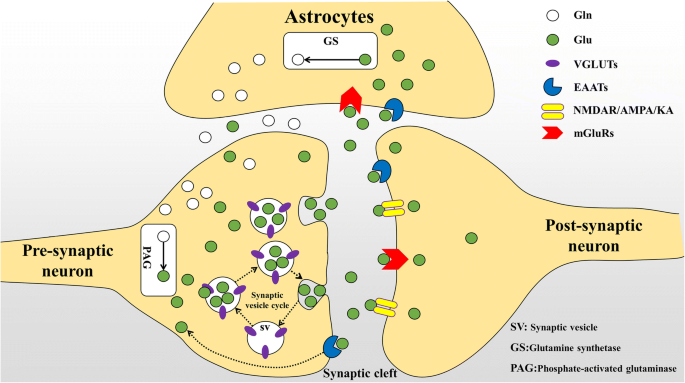
Research progress on the role of type I vesicular glutamate transporter (VGLUT1) in nervous system diseases, Cell & Bioscience

2 Overview of the Glutamatergic System, Glutamate-Related Biomarkers in Drug Development for Disorders of the Nervous System: Workshop Summary

Modulation of Synaptic Plasticity by Glutamatergic Gliotransmission: A Modeling Study
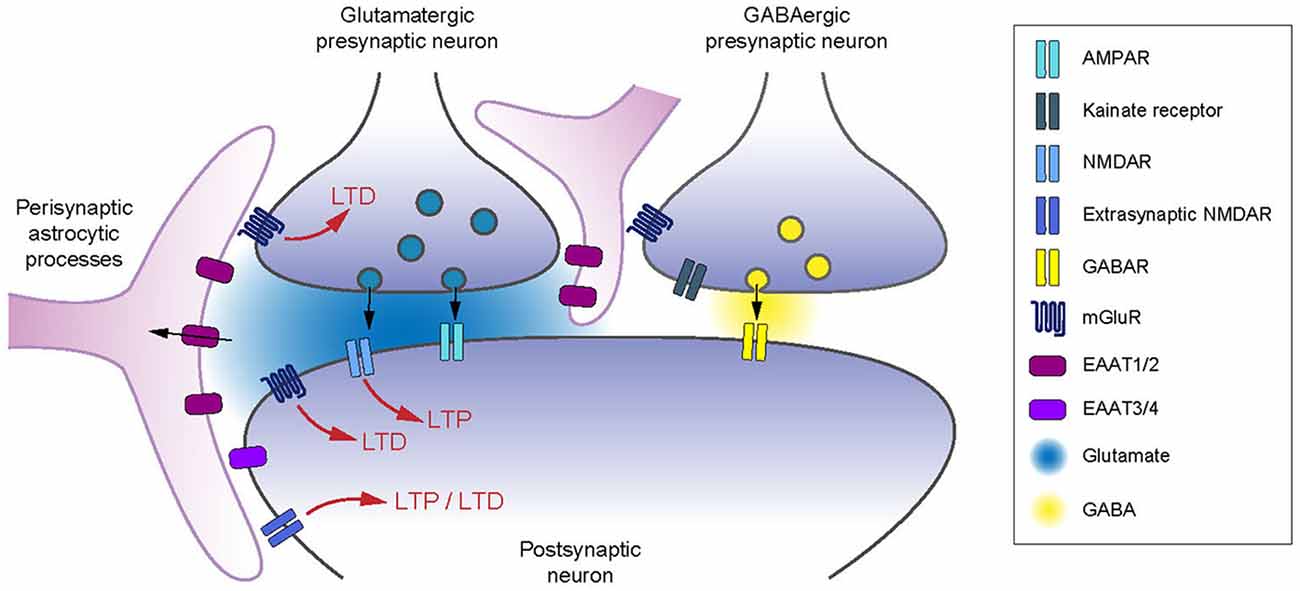
Frontiers Control of Long-Term Plasticity by Glutamate Transporters

Shaping of Signal Transmission at the Photoreceptor Synapse by EAAT2 Glutamate Transporters

Infographic: How a Glutamate Sensor Tracks Synapses

The Role of the Tripartite Glutamatergic Synapse in the Pathophysiology and Therapeutics of Mood Disorders

GABA Enhances Transmission at an Excitatory Glutamatergic Synapse