Convergent zones of cortical and subcortical large terminals in
4.6 (446) · € 18.00 · En Stock
Download scientific diagram | Convergent zones of cortical and subcortical large terminals in POm. (A) Distribution of large cortical (black dots; 1 dot = 2 boutons) and subcortical terminals (yellow outline) labeled by anterograde tracing and vGlut2 immunostaining, respectively, in the whole rostro-caudal extent (1-6, rostral to caudal) of rat POm (blue outline) in a representative animal. Yellow outline indicates vGlut2 rich zones. (for definition, see Materials and Methods section). Note the occurrence of large cortical terminals within as well as outside of the vGlut2 rich zones. Percentages represent the fraction of POm area rich in large vGlut2 terminals. (B and C) Convergent and nonconvergent zones in rat (B and D) and mouse (C-E). In B-E, black rectangles show the position of the high-power light microscopic images (B1-E1). In convergent zones (B1 and C1), large PHAL-labeled (black) cortical terminals (arrows) are in close proximity to vGLUT2-immunoreactive (brown) subcortical terminals (arrowheads). In nonconvergent zones (D1 and C1), only large cortical terminals are visible (arrows) subcortical terminals are absent or occur in low numbers. Note that cortical terminals originating from layer 6 are considerably smaller in size than giant layer 5 boutons (the red framed areas show a group of small PHAL-labeled boutons in C1 and D1). Scale bar, A: 500 μm; B1-D1: 20 μm. from publication: Convergence of Cortical and Sensory Driver Inputs on Single Thalamocortical Cells | Ascending and descending information is relayed through the thalamus via strong, “driver” pathways. According to our current knowledge, different driver pathways are organized in parallel streams and do not interact at the thalamic level. Using an electron microscopic | Cortical, Nucleus and Thalamus | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Convergence of location, direction, and theta in the rat

PDF) Converging Structural and Functional Connectivity of

Integration of two large-scale anatomical datasets to investigate

Rapid Cortical Plasticity Supports Long-Term Memory Formation

Schematics demonstrating convergence of cortical projections from

Convergent zones of cortical and subcortical large terminals in
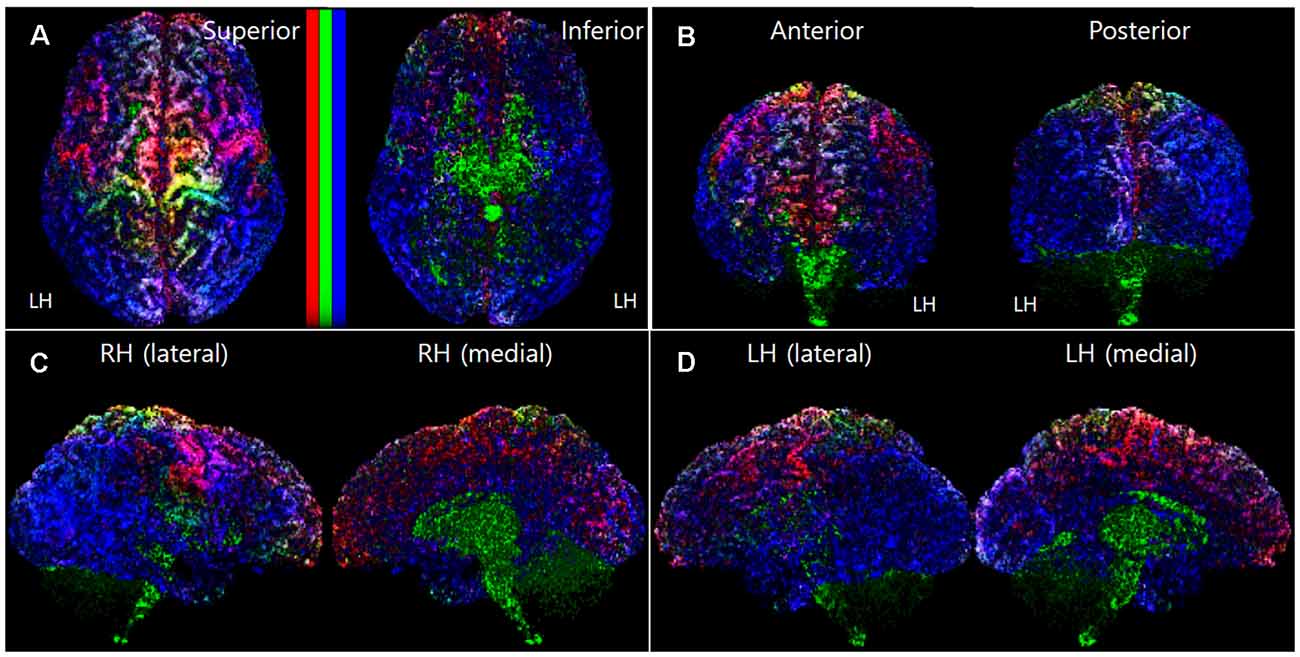
Frontiers Track-Density Ratio Mapping With Fiber Types in the
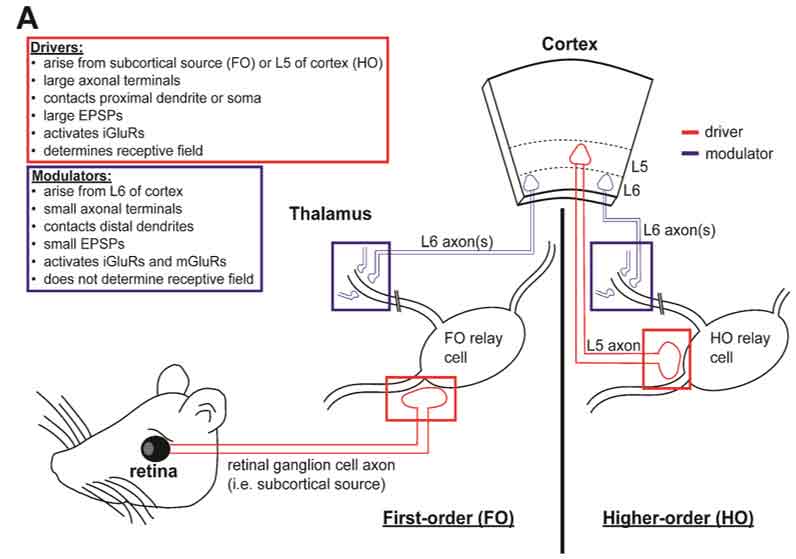
Morphological variation among corticothalamic terminals implies

Drivers of the Primate Thalamus

Reduced thalamic excitation to motor cortical pyramidal tract

Cortical responses to touch reflect subcortical integration of

Conserved patterns of functional organization between cortex and
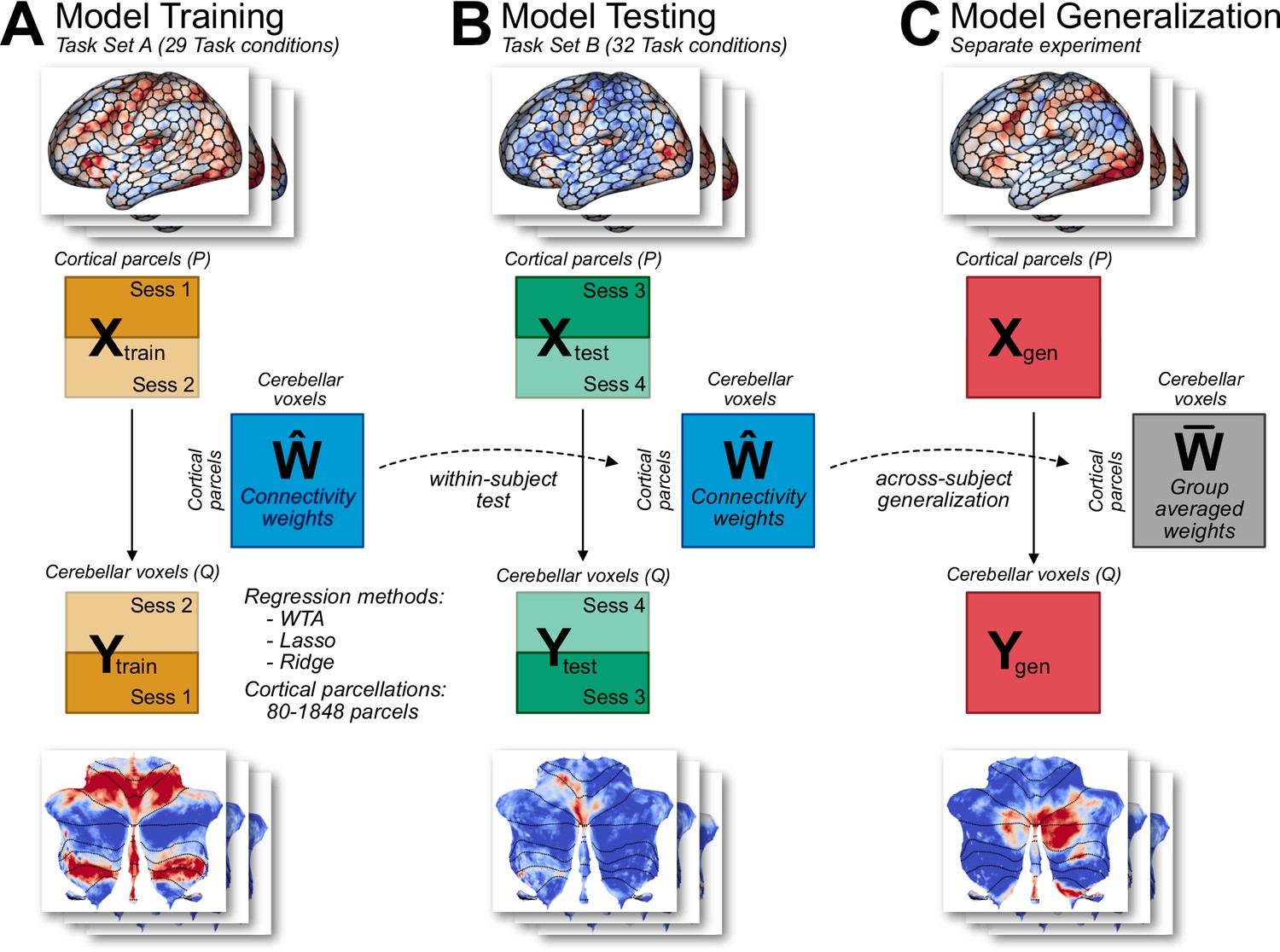
A task-general connectivity model reveals variation in convergence
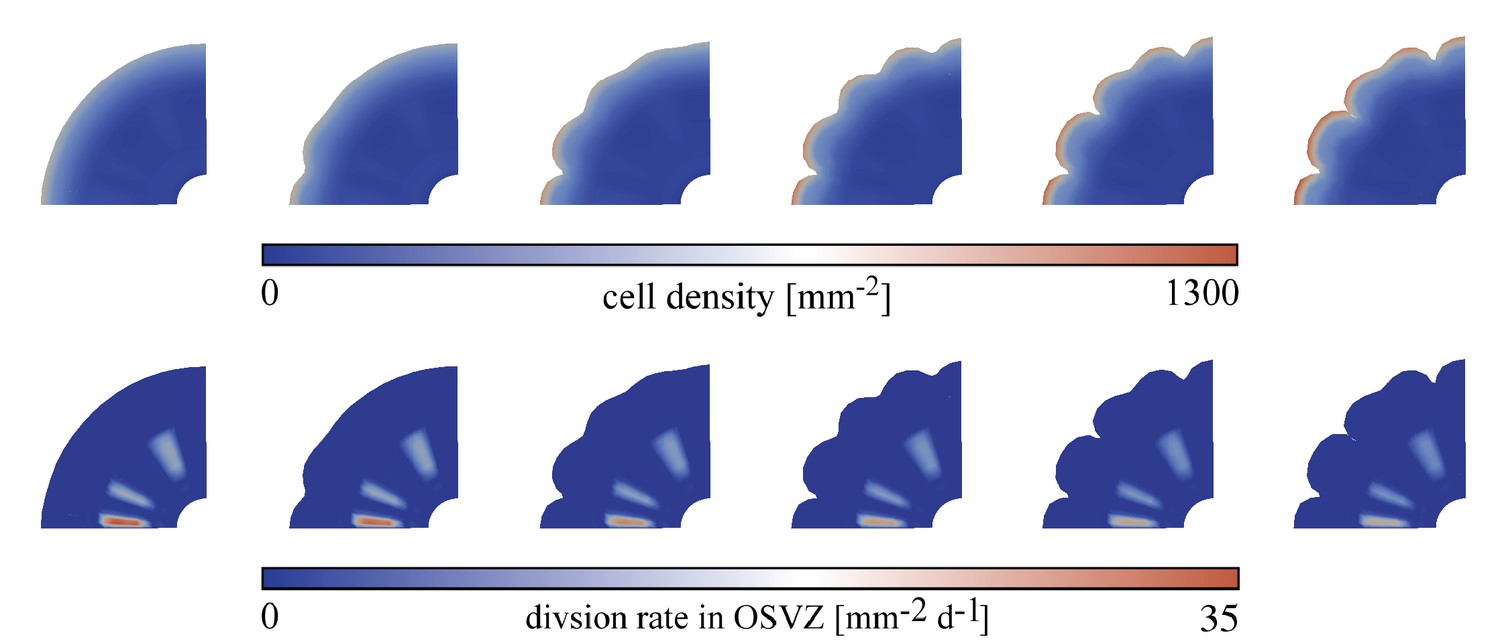
Exploring the role of the outer subventricular zone during

ChR2-EYFP-positive large cortical terminals from barrel cortex












